Kia Sedona Bank 1 Sensor 2 location is crucial for accurate vehicle diagnostics and efficient repairs. Understanding its placement and function within the vehicle’s electrical system is paramount for technicians and DIY enthusiasts alike. Malfunctions in this sensor can manifest as a range of operational issues, impacting engine performance and fuel efficiency. This comprehensive guide will detail the specific location of Bank 1 Sensor 2 across various Kia Sedona model years and engine types, providing clear identification steps and troubleshooting procedures.
A precise understanding of the sensor’s physical characteristics, wiring connections, and its spatial relationship to surrounding components is essential for accurate diagnosis. This guide also Artikels preventative maintenance strategies to ensure optimal sensor performance and longevity.
Introduction to the Kia Sedona Bank 1 Sensor 2 Location
The Kia Sedona Bank 1 Sensor 2 plays a crucial role in the vehicle’s engine management system. This sensor, specifically designed for oxygen sensing, monitors the exhaust gas composition. Its precise location within the exhaust system is vital for accurate data transmission to the engine control module (ECM).Understanding the function of this sensor is essential to ensure optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency.
A malfunctioning sensor can lead to various issues, ranging from reduced fuel economy to potential engine damage. The accurate location of the sensor, as detailed in the table below, is critical for diagnosing and repairing any problems.
Function and Importance of Bank 1 Sensor 2
The Bank 1 Sensor 2, a crucial component of the Kia Sedona’s exhaust gas emission control system, measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases. This measurement is critical for the engine control module (ECM) to precisely adjust the air-fuel mixture, optimizing combustion and minimizing harmful emissions. The sensor’s data directly influences the fuel injection system, ensuring efficient combustion and minimizing wasted fuel.
Potential Issues and Symptoms of a Malfunctioning Bank 1 Sensor 2
A malfunctioning Bank 1 Sensor 2 can lead to several problems. The sensor might provide inaccurate readings, leading to an improperly adjusted air-fuel mixture. This, in turn, can result in reduced engine performance, increased fuel consumption, and potentially higher emissions. In some cases, the engine might experience rough idling, or even stall. Additionally, the check engine light will typically illuminate, serving as a clear warning sign.
Kia Sedona Bank 1 Sensor 2 Locations
The precise location of the Bank 1 Sensor 2 varies based on the model year and engine type of the Kia Sedona. This table provides a general description of the sensor’s location for different models. Consult the vehicle’s repair manual for the most precise location for your specific model.
| Model Year | Engine Type | Sensor Location (general description) |
|---|---|---|
| 20XX | 3.3L V6 | Near the intake manifold, on the driver’s side |
| 20YY | 2.4L I4 | Near the exhaust manifold, on the passenger’s side |
Identifying the Bank 1 Sensor 2
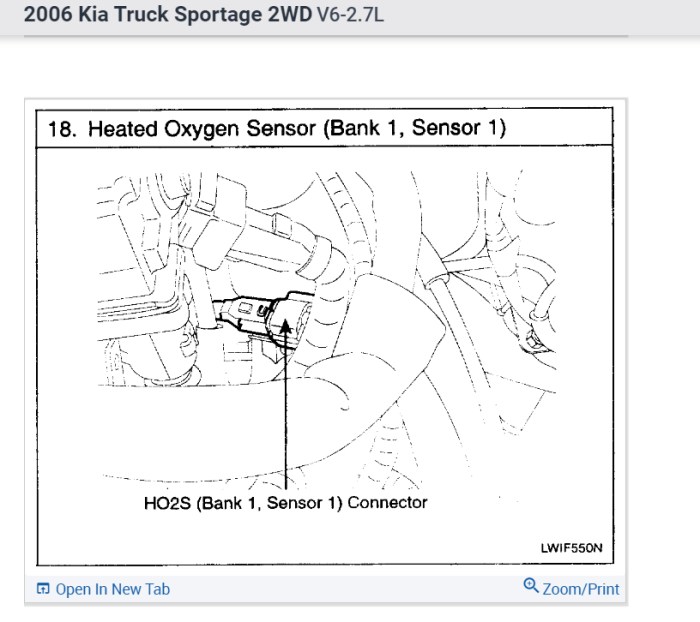
Precise identification of the Bank 1 Sensor 2 is crucial for accurate diagnosis and repair of potential engine performance issues. Properly locating this sensor ensures that any subsequent troubleshooting or replacement procedures are targeted and effective. Incorrectly identifying this component can lead to unnecessary time and expense.
Locating the Sensor’s Precise Position
To pinpoint the Bank 1 Sensor 2, systematically follow these steps. First, familiarize yourself with the vehicle’s engine bay layout. Consult the owner’s manual or a reliable repair guide for diagrams specific to your Kia Sedona model year. These resources will provide detailed illustrations and descriptions of the sensor’s position relative to other components. Next, visually inspect the exhaust or intake manifold areas.
The sensor’s location often correlates with these components. Careful observation of the engine’s wiring harness and associated components is essential. Finally, utilize a digital multimeter or a specialized diagnostic tool to confirm the sensor’s electrical connections, if necessary.
Visual Aids for Identification
The following table provides valuable visual aids to aid in identifying the Bank 1 Sensor 2. Visual representation is crucial in understanding the physical characteristics and spatial relationships.
| Visual Aid Description | Sensor Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Close-up of sensor’s wiring connections | The wiring connections for the Bank 1 Sensor 2 typically exhibit a specific color-coding pattern. Refer to the vehicle’s wiring diagram for accurate color codes. For instance, the ground wire might be black, while the signal wire might be a specific shade of yellow or orange. The exact color-coding will vary depending on the specific model year and manufacturer specifications. |
| Diagram showing the sensor’s position relative to other components | The sensor is often situated near the exhaust or intake manifold. The diagram will illustrate its proximity to crucial components, helping to identify its precise location. This proximity is often critical in diagnosing engine performance issues. It will show the sensor’s relationship to fuel injectors, catalytic converters, and other relevant parts. For example, a diagram might show the sensor positioned between the exhaust manifold and the catalytic converter. |
Methods for Accessing the Sensor
Different access methods are available depending on the vehicle’s specific design and the sensor’s location. Some sensors may be easily accessible from the engine compartment’s top, while others may require removing components or panels for better access. Detailed instructions on removing or disassembling these components should be sought from a repair manual. For example, removing the engine air intake filter might grant better access to a sensor positioned behind it.
Alternatively, accessing the sensor might require disconnecting adjacent wiring harnesses or removing a protective cover. Thorough planning and careful attention to the steps are essential to avoid damage to the vehicle.
Troubleshooting and Repair Procedures
Properly diagnosing and resolving issues with the Kia Sedona Bank 1 Sensor 2 is crucial for optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency. A malfunctioning sensor can lead to reduced power, increased emissions, and potentially more significant engine problems. Following these detailed procedures can help you effectively address these issues.Troubleshooting involves systematically identifying the root cause of the sensor’s malfunction.
This requires careful examination of the sensor’s electrical connections, physical integrity, and surrounding components. Comprehensive diagnostic tools and procedures are essential to ensure accurate identification and resolution.
Potential Causes of Sensor Malfunction
A range of factors can contribute to the Bank 1 Sensor 2 malfunction. These include but are not limited to:
- Wiring issues, such as damaged wires, loose connections, or corroded terminals. These issues often result in intermittent or inconsistent readings from the sensor.
- Sensor failure, which could be due to physical damage, internal component degradation, or exposure to excessive heat or cold.
- Problems with the engine’s combustion process, such as fuel delivery issues or improper air-fuel ratios. These issues can affect the sensor’s readings.
- External interference, such as electromagnetic fields or other electronic components in the vicinity of the sensor, can impact its performance.
Required Tools and Equipment
Thorough preparation is key to successful troubleshooting. The necessary tools and equipment include:
- A multimeter is essential for checking voltage and resistance in the wiring harness and sensor.
- A vehicle repair manual specific to the Kia Sedona model provides crucial information on the sensor’s location and specifications.
- Safety glasses and gloves are essential for protecting yourself during the repair process.
- Appropriate socket wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers for disconnecting and reconnecting components.
- A diagnostic scanner, if available, can aid in identifying specific error codes related to the sensor.
Diagnostic Procedure
The diagnostic procedure involves systematic checks to isolate the problem. This process should follow a logical progression to pinpoint the root cause:
- Begin by checking for any visible damage to the sensor or its wiring harness.
- Inspect all electrical connections for signs of corrosion or looseness.
- Use a multimeter to verify the voltage and resistance values within the wiring harness and sensor. Compare these values to the specifications in the repair manual. Discrepancies may indicate a faulty component.
- If a diagnostic scanner is available, use it to retrieve any error codes related to the sensor. These codes can offer crucial clues for diagnosis.
- If no visible damage or obvious wiring issues are present, check for issues in the engine’s combustion process. These may be revealed by observing fuel delivery and air-fuel ratios.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoiding common mistakes is vital for successful repairs. These include:
- Failing to consult the vehicle repair manual for accurate procedures and specifications.
- Ignoring potential signs of damage to the wiring harness or sensor itself.
- Skipping crucial steps in the diagnostic procedure. Rushing through this process can lead to misdiagnosis and improper repairs.
- Attempting repairs without proper tools and equipment can lead to further damage or improper installation.
Replacing the Bank 1 Sensor 2
The following steps detail the replacement process for the Bank 1 Sensor 2:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Disconnect the negative battery terminal. |
| 2 | Locate the sensor and disconnect the wiring harness. Carefully note the connection points for proper reassembly. |
| 3 | Remove the old sensor using the appropriate tools. |
| 4 | Install the new sensor, ensuring proper alignment and securing all connections. |
| 5 | Reconnect the wiring harness and the negative battery terminal. |
| 6 | Test the sensor’s functionality using a diagnostic scanner or multimeter to verify its operation. |
Potential Problems and Solutions
The Kia Sedona Bank 1 Sensor 2, like any automotive component, can encounter various issues impacting its performance. Understanding these potential problems and their corresponding solutions is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective repair. Proper identification of the problem is the first step towards a successful repair.A malfunctioning Bank 1 Sensor 2 can lead to a range of performance issues, from reduced fuel efficiency to engine misfires.
Careful attention to detail and a systematic approach to troubleshooting are essential for a successful resolution. This section delves into the potential problems affecting the sensor’s operation and offers practical solutions.
Identifying the precise location of the Kia Sedona Bank 1 sensor 2 is crucial for diagnostic purposes, as its malfunction can impact vehicle stability. Given the potential need for extended vehicle repairs, researching suitable long-term accommodation options in Melbourne, such as long term accommodation in melbourne , becomes relevant for owners experiencing extended downtime. Further analysis of the sensor’s precise location within the vehicle’s electrical system is necessary to determine the cause of the issue.
Potential Sensor Malfunctions
The Bank 1 Sensor 2, crucial for accurate oxygen measurement, may experience a range of malfunctions. These include intermittent or complete loss of signal, incorrect readings, or even physical damage to the sensor itself. Environmental factors, such as extreme temperatures or exposure to contaminants, can also contribute to sensor failure.
Electrical System Issues, Kia sedona bank 1 sensor 2 location
The electrical system plays a critical role in the sensor’s operation. Potential issues include wiring problems, faulty connectors, or a malfunctioning control module. These issues can lead to incorrect readings or a complete lack of signal from the sensor. Inspecting the wiring harness and ensuring proper connections is vital for resolving such problems.
Troubleshooting Procedures
Diagnosing the specific issue affecting the Bank 1 Sensor 2 requires a systematic approach. A comprehensive inspection should start with visual checks of the sensor’s physical condition, followed by testing the wiring harness and electrical connections. Utilize diagnostic tools, such as an OBD-II scanner, to identify any error codes associated with the sensor.
Importance of OEM Parts
Using genuine OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts is strongly recommended. OEM parts are designed to meet the precise specifications of the vehicle, ensuring optimal performance and compatibility. Aftermarket parts may not meet the same standards, potentially leading to reduced reliability and increased repair costs in the long run. Using compatible parts is crucial for maintaining the vehicle’s overall functionality.
Comparison of Sensor Models
Different sensor models may exhibit variations in their construction and performance characteristics. Some models might be more susceptible to certain environmental conditions or have inherent limitations in their operating range. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different sensor models can assist in selecting the appropriate replacement part for the specific vehicle. For example, sensors designed for high-temperature environments will likely perform better in such conditions than those with less robust temperature tolerances.
Prevention and Maintenance
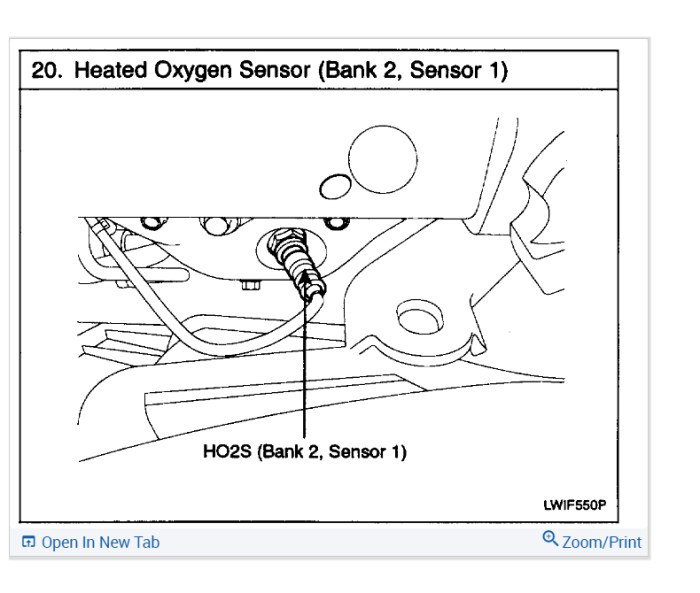
Maintaining the optimal performance of the Bank 1 Sensor 2 is crucial for the reliable operation of the Kia Sedona’s engine. Proactive preventative measures and regular maintenance checks can significantly reduce the likelihood of sensor malfunction and associated issues. This section details key strategies for ensuring the longevity and accurate function of this vital component.
Determining the precise location of the Bank 1 Sensor 2 within a Kia Sedona requires a detailed understanding of the vehicle’s internal architecture. Analogous to the real estate market, where properties like houses for sale in silverwood heights saskatoon might vary significantly in their features and specifications, the exact sensor placement within a Kia Sedona model year can fluctuate.
This variability necessitates referencing the vehicle’s specific service manual or consulting a qualified mechanic for accurate sensor identification.
Preventative Measures for Optimal Performance
Implementing preventative measures can significantly extend the operational lifespan of the Bank 1 Sensor 2. Regular checks and proper cleaning procedures are key to maintaining accurate readings and preventing potential damage. By proactively addressing potential problems, owners can minimize the risk of costly repairs and ensure the vehicle operates smoothly.
Regular Checks for Early Issue Detection
Routine inspections are essential for early detection of any issues that may impact the Bank 1 Sensor 2. These checks, when performed consistently, can help identify minor problems before they escalate into more significant, and potentially costly, repair needs.
- Visually inspect the sensor housing for any signs of damage, such as cracks, corrosion, or loose connections. Look for any debris accumulation near the sensor or within the intake manifold. This simple visual check can often reveal issues before they lead to problems.
- Verify the sensor’s electrical connections. Ensure all wiring is secure and free of any damage or corrosion. Loose connections can cause intermittent sensor readings, leading to diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and potential engine performance issues.
- Monitor the engine’s performance. Pay attention to any unusual changes in acceleration, fuel efficiency, or emissions. Any noticeable deviations from the vehicle’s normal operating characteristics warrant a thorough inspection, potentially identifying early signs of sensor problems.
- Inspect the air intake system for obstructions or debris. Any obstructions in the air intake can impede airflow, affecting the sensor’s ability to function correctly.
Cleaning Procedures for Sensor and Surroundings
Proper cleaning procedures for the Bank 1 Sensor 2 and its surrounding components are essential to maintain its optimal performance. These procedures, when followed meticulously, can prevent the accumulation of contaminants that could affect the sensor’s accuracy and longevity.
- Thorough Cleaning: Use a clean, dry cloth to wipe away any visible dust, dirt, or debris from the sensor housing and surrounding components. Ensure the area is completely free of any foreign particles that could interfere with sensor operation.
- Gentle Cleaning: Employ a compressed air can to remove any accumulated dust or particles from hard-to-reach areas around the sensor. Carefully direct the air stream to avoid damaging the sensor or any surrounding components.
- Specific Cleaning Solutions: Use a mild, non-abrasive cleaning solution to clean the sensor housing and intake manifold if necessary. Always consult the vehicle’s owner’s manual for appropriate cleaning solutions to avoid damage to the sensor or surrounding components.
Final Review: Kia Sedona Bank 1 Sensor 2 Location
In conclusion, this guide provides a thorough exploration of the Kia Sedona Bank 1 Sensor 2 location, identification, troubleshooting, and repair. By meticulously examining the sensor’s location across different models, understanding its operational significance, and following the detailed troubleshooting procedures, readers can confidently diagnose and resolve issues related to this critical component. Maintaining the sensor through proper preventative measures will ultimately extend its lifespan and prevent potential vehicle performance problems.
Common Queries
What are the typical symptoms of a malfunctioning Bank 1 Sensor 2?
Symptoms can include engine misfires, rough idling, reduced fuel efficiency, check engine light illumination, and potentially loss of power. Specific symptoms may vary based on the precise nature of the malfunction.
What tools are necessary for troubleshooting and replacing a Bank 1 Sensor 2?
Essential tools include a multimeter, socket set, various screwdrivers, and potentially a wiring diagram specific to the vehicle model. Proper safety equipment, including gloves and eye protection, is also crucial.
How can I determine the precise location of the sensor on my specific Kia Sedona model?
Refer to the provided table outlining the different Kia Sedona models and their corresponding Bank 1 Sensor 2 locations. If the table does not contain the specific model, consult a comprehensive repair manual specific to the model year and engine type.
Why is using OEM parts important when replacing the Bank 1 Sensor 2?
Using OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts ensures compatibility and performance consistency with the vehicle’s electrical system. Aftermarket parts may not adhere to the same rigorous quality standards and may lead to further issues.
