Ownership of a life insurance policy may be temporarily transferred, often during loan arrangements or trust setups. This temporary ownership alters the policyholder’s rights and responsibilities, impacting cash value, premiums, death benefits, and more. Understanding the legal frameworks, practical implications, and procedures involved is crucial for both policyholders and temporary owners.
This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of temporary life insurance policy ownership, from defining temporary versus permanent ownership to detailing the legal requirements, practical implications for policyholders, and the procedures involved in transferring ownership. We’ll also examine insurance company policies and provide illustrative case studies.
Understanding Temporary Ownership

A fleeting shadow of possession, a temporary tenure over life’s uncertain currents. This fragile grasp, this ownership in transit, holds a unique place in the labyrinthine world of financial agreements, a nuanced dance between rights and responsibilities. The echoes of past promises and future uncertainties linger in the air, whispering tales of loans, trusts, and the shifting sands of life’s unforeseen turns.Temporary ownership of a life insurance policy differs fundamentally from permanent ownership, a stark contrast marked by duration and control.
It’s a conditional arrangement, a temporary entrustment, often a means to a specific end, a bridge across a financial chasm. The legal and contractual implications are meticulously crafted, ensuring the temporary owner’s rights are defined, while the policy’s ultimate beneficiary remains protected.
Definition of Temporary Ownership
Temporary ownership of a life insurance policy is a contractual arrangement where an individual or entity gains control of the policy for a specific period. This differs from permanent ownership, which entails full and enduring control. Crucially, temporary ownership doesn’t grant the same level of rights and responsibilities as permanent ownership. This temporary tenure is usually limited by the terms of a loan, trust, or other legal agreement.
Legal and Contractual Implications
The legal and contractual implications of temporary policy ownership are meticulously defined within the agreement. The temporary owner’s rights and responsibilities are clearly Artikeld, usually restricting them from certain actions like surrendering the policy or changing the beneficiary designations. The terms of the agreement dictate the specific limitations.
Scenarios of Temporary Ownership
Temporary ownership frequently arises in situations involving loans secured by the policy or trust arrangements where the policy is held temporarily for the benefit of a beneficiary. For example, a parent might place a policy in a trust for a child, granting temporary ownership to the trustee. Or, a policy might be temporarily transferred to a lender as collateral for a loan, with the temporary owner obligated to maintain the policy’s status until the loan is repaid.
Difference Between Temporary Ownership and Beneficiary Designations
Beneficiary designations, in contrast, dictate who receives the policy’s payout upon the insured’s death. Temporary ownership, on the other hand, is about the policy’s control during a specific period, while the beneficiary’s rights remain unchanged. Temporary ownership affects the rights of the policyholder during the period of the agreement.
Table: Temporary vs. Permanent Ownership
| Characteristic | Temporary Ownership | Permanent Ownership | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Duration | Limited, specific time frame | Indefinite, lasting | Temporary ownership is for a defined period, while permanent ownership is perpetual. |
| Control | Restricted, often by agreement | Full and absolute | Temporary ownership is constrained by the agreement, while permanent ownership allows for complete control. |
| Rights | Artikeld by the agreement | Broad, including policy management | The temporary owner’s rights are explicitly defined in the agreement, whereas permanent ownership grants wide-ranging rights. |
| Responsibilities | Artikeld by the agreement | Full policy maintenance | Responsibilities are Artikeld in the agreement for temporary ownership, while permanent ownership necessitates full policy maintenance. |
Legal Frameworks and Regulations
A fragile shadow falls across the landscape of life insurance, where temporary ownership casts a mournful hue. The legal frameworks governing these arrangements are intricate, woven with threads of protection and potential peril. Navigating these legal labyrinths requires a discerning eye, for the fate of a policy’s value hangs precariously in the balance.The legal tapestry surrounding life insurance policies and temporary ownership arrangements is richly embroidered with diverse regulations.
Jurisdictions worldwide employ differing legal standards, resulting in a complex and nuanced landscape. Understanding these differences is crucial to mitigating potential legal disputes.
Legal Frameworks Governing Life Insurance Policies
Different jurisdictions utilize varying legal frameworks to govern life insurance policies. These frameworks establish the rights and obligations of policyholders, beneficiaries, and insurers. The legal structures determine the validity and enforceability of temporary ownership arrangements. These frameworks are crucial in maintaining the integrity of the insurance system and safeguarding policyholders’ interests.
Regulations Governing Transfer of Ownership Rights
Regulations governing the transfer of ownership rights in life insurance policies vary significantly across jurisdictions. These regulations often necessitate specific documentation, notarization, or approval from regulatory bodies. Strict adherence to these regulations is vital to ensure a legally sound transfer of ownership. Failure to comply can lead to the invalidation of the temporary ownership arrangement.
Role of Regulatory Bodies in Overseeing Temporary Ownership Transactions
Regulatory bodies play a critical role in overseeing temporary ownership transactions in life insurance policies. Their oversight is intended to maintain the integrity of the insurance market and protect policyholders. These bodies establish standards, review transactions, and investigate complaints. Their vigilance is crucial in safeguarding the interests of all parties involved.
Common Legal Issues Related to Temporary Ownership
Several legal issues frequently arise in connection with temporary ownership arrangements. These include disputes over the validity of the transfer, disagreements concerning the terms of the temporary arrangement, and conflicts over the policy’s ultimate disposition. Understanding these potential pitfalls is vital for avoiding costly legal battles.
Comparison of Regulations for Temporary Ownership in Various Countries
The regulations for temporary ownership in life insurance policies differ significantly across various countries. The legal frameworks and regulations governing these arrangements vary considerably, leading to distinct approaches to temporary ownership. These variations stem from diverse cultural, economic, and historical factors.
Table Summarizing Legal Requirements for Temporary Ownership
| Jurisdiction | Documentation Required | Regulatory Approval | Dispute Resolution Mechanisms |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Signed ownership transfer documents, often notarized | State insurance departments may require specific approvals | State courts and administrative procedures |
| United Kingdom | Formal transfer documents, registered with the insurer | Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) oversight | Civil courts and arbitration |
| Canada | Signed ownership transfer documents, specific forms depending on the province | Provincial insurance commissions | Provincial courts and dispute resolution centers |
| Japan | Designated forms for policy transfer, insurer approval required | Insurance regulator | Civil courts, administrative procedures |
This table provides a limited overview. Specific legal requirements and procedures can differ significantly within each jurisdiction. Always consult with legal counsel for accurate and up-to-date information.
Practical Implications for Policyholders
A shadowed veil descends upon the life insurance policy, where temporary ownership casts its somber spell. The once-familiar comfort of control now shimmers with uncertainty, a fragile bloom threatened by the frost of change. This temporary arrangement, though perhaps necessary, alters the landscape of rights and responsibilities, demanding a careful assessment of its practical ramifications.
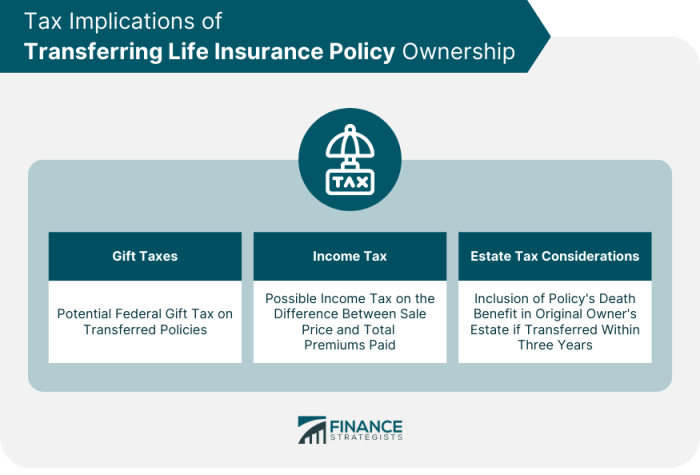
Tax Implications
Temporary ownership can trigger complex tax implications for the policyholder. Changes in ownership often necessitate adjustments to tax reporting, potentially leading to unforeseen tax liabilities or deductions. The specifics vary depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the temporary transfer. Understanding these nuances is crucial for accurate financial planning.
Impact on Policy Benefits
The temporary transfer of ownership may affect the policyholder’s entitlement to policy benefits. The temporary owner may have limited rights to the policy’s cash value or surrender value. The original policyholder may be restricted in accessing these funds until the temporary ownership period concludes. These limitations must be considered carefully.
Impact on Policy’s Cash Value and Premium Payments
The cash value accumulation and the frequency of premium payments are directly impacted by the temporary transfer. The temporary owner might not be entitled to the same level of cash value growth as the original owner. Premium payments, too, may experience shifts in terms and conditions. These shifts can affect the policy’s overall financial health.
Impact on Death Benefit and Beneficiary Rights
Temporary ownership often impacts the death benefit and the rights of the designated beneficiary. The temporary owner’s rights to claim the death benefit may be restricted. The original policyholder may retain control over the beneficiary designation, or the temporary owner might have the right to alter the beneficiary designation. The impact on beneficiary rights necessitates careful scrutiny.
Impact on Policy’s Surrender Value and Loan Options
The surrender value of the policy and the availability of loans are significantly affected by the temporary ownership arrangement. The temporary owner might have limited access to these options. The original policyholder’s rights to these features might be restricted. These restrictions necessitate a thorough understanding of the terms and conditions.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks of Temporary Ownership
| Factor | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks | Illustrative Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tax Implications | Potential tax deductions or favorable tax treatment in specific scenarios. | Unforeseen tax liabilities or increased tax burden. | Tax implications differ based on the jurisdiction, the nature of the transfer, and the specific terms of the agreement. |
| Policy Benefits | Temporary access to specific benefits, like cash value access. | Limited access to policy benefits during the temporary period. | A policyholder may temporarily grant access to a cash value loan to a family member. |
| Cash Value & Premiums | Potential access to policy cash value. | Potential restrictions on premium payments or cash value growth during the temporary period. | A business might temporarily take over a policy to fund an employee benefit package. |
| Death Benefit & Beneficiaries | Potential for temporary adjustments to death benefit distribution. | Restrictions on beneficiary rights and the right to alter the beneficiary designation. | A parent might temporarily transfer ownership to a child to secure a specific inheritance plan. |
| Surrender Value & Loans | Temporary access to surrender value or loans under specific conditions. | Limited access to surrender value or loans during the temporary ownership period. | A policyholder might temporarily grant access to a loan to fund a significant purchase. |
Transactions and Procedures
A fragile, fleeting tenure, this temporary ownership, a shadow cast upon the enduring contract. The life insurance policy, a solemn promise, now bears the imprint of a shifting hand. The meticulous steps to effect this temporary transfer are like the measured breaths of a grieving soul, each one carrying a weight of responsibility.The procedure for transferring temporary ownership of a life insurance policy demands a precise sequence of actions.
Every step, a testament to the need for clarity and meticulous record-keeping. The transition from one custodian to another must be documented with scrupulous care, a silent guarantee against future uncertainty.
Detailed Procedure for Transfer
A carefully orchestrated dance of paperwork and procedures must be followed. Failure to adhere to the Artikeld steps may result in delays or rejection of the request.
The transfer of temporary ownership necessitates a formal application submitted to the insurance company, clearly outlining the duration and terms of the temporary arrangement.
- Application Submission: The temporary owner submits a comprehensive application form, detailing the specifics of the temporary transfer. This includes the policy number, the temporary owner’s identity, the duration of the temporary ownership, and the reasons for the transfer.
- Document Verification: The insurance company meticulously verifies the authenticity of the documents provided by the temporary owner. This includes verifying the identity and legal standing of the temporary owner, as well as the validity of the supporting documents.
- Policy Review and Approval: The insurance company reviews the policy and the submitted documentation. This process often involves scrutinizing the policy’s provisions and ensuring the transfer aligns with the terms of the agreement.
- Transfer Execution: Following approval, the insurance company executes the temporary ownership transfer, updating its records accordingly.
- Notification: The temporary owner and the previous owner receive formal notifications confirming the transfer of temporary ownership.
Required Documents
The transfer process hinges on the accuracy and completeness of the provided documents. Errors or omissions may lead to delays or rejection of the transfer request.
- Proof of Identity: A valid government-issued photo identification document, such as a passport or driver’s license, is crucial for establishing the temporary owner’s identity.
- Proof of Relationship (if applicable): In situations where the temporary owner is a relative or legal representative, supporting documentation proving the relationship or legal authority is necessary.
- Policy Documents: The original policy document or a certified copy is required for verification.
- Application Form: A duly completed application form, specifically designed for temporary ownership transfers, must be submitted.
Role of Insurance Companies
The insurance company acts as the impartial gatekeeper, ensuring the smooth and secure transition of temporary ownership.
Temporary ownership of a life insurance policy can arise in various circumstances. For example, individuals interested in high-performance vehicles might consider the hot rods for sale in melbourne market, potentially impacting their policy’s ownership. However, the temporary nature of this ownership, for whatever reason, will still affect the policy’s validity and associated rights.
- Verification and Validation: The insurance company verifies the legitimacy of the transfer request by examining the provided documents.
- Record Keeping: The insurance company maintains accurate records of the temporary ownership transfer, safeguarding against future disputes.
- Communication: The insurance company communicates the status of the transfer request to the involved parties.
Accurate Record-Keeping
Maintaining detailed records throughout the temporary ownership period is vital. This meticulous record-keeping is crucial for safeguarding the policy and the rights of all parties involved.
- Documentation of all communications: Any correspondence with the insurance company regarding the transfer should be meticulously documented.
- Regular policy updates: Regularly review the policy documents to ensure any changes or amendments are noted.
Timeline for Transfer
The timeline for the transfer of temporary ownership varies depending on the complexity of the request and the responsiveness of the insurance company.
- Processing Time: The processing time is usually between 10 to 30 business days, but may vary depending on the specific circumstances and the insurance company’s internal processes.
Verification of Temporary Owner’s Identity
Verification of the temporary owner’s identity is a critical aspect of the process. This process prevents fraudulent activities.
- Government-issued identification: A valid government-issued photo identification is a standard requirement.
- Confirmation of address: Confirmation of the temporary owner’s current address is usually required to prevent identity theft and ensure the accuracy of the transfer.
Step-by-Step Transfer Guide
The following steps provide a general guide. Consult with the insurance company for specific requirements.
- Gather all necessary documents.
- Complete the application form accurately and completely.
- Submit the application and documents to the insurance company.
- Follow up with the insurance company for the status of the transfer.
- Retain copies of all correspondence and documents related to the transfer.
Insurance Company Policies
A shroud of uncertainty hangs over temporary ownership, a fleeting grasp on something precious. The policies of insurance companies, like solemn pronouncements, dictate the terms of this fragile arrangement. Each company, with its own internal logic, sets the parameters, weaving a tapestry of rights and restrictions.
Policies Regarding Temporary Ownership Arrangements
Insurance companies maintain differing policies concerning temporary ownership. These policies reflect a complex interplay of legal obligations, financial considerations, and the inherent risks associated with temporary transfers of control. Some companies view temporary ownership as a specialized niche, whereas others may perceive it as a frequent occurrence. Understanding these varied approaches is crucial for policyholders navigating this often-complex terrain.
Specific Clauses and Provisions
Policies often contain clauses outlining the conditions under which temporary ownership is permitted. These clauses specify the duration of the temporary transfer, the specific individuals or entities authorized to exercise ownership rights, and the procedures for initiating and concluding the arrangement. They also typically Artikel responsibilities and limitations. Examples of these provisions include stipulations regarding the temporary holder’s liability, the payment of premiums during the temporary transfer, and the procedures for restoring the original ownership structure.
A clear understanding of these clauses is vital to avoid potential pitfalls.
Common Requirements for Temporary Ownership
Various requirements are commonly imposed by insurance companies for temporary ownership. These requirements may include, but are not limited to, documentation of the temporary holder’s identity and financial stability, a written agreement specifying the terms of the temporary arrangement, and the provision of specific contact information. Each insurance company formulates its own set of requirements to ensure the safety and security of the policy.
The meticulous adherence to these guidelines is essential for a smooth transition.
Exceptions and Limitations
Certain exceptions and limitations frequently apply to temporary ownership arrangements. These exceptions often relate to specific policy types, geographic restrictions, or pre-existing conditions. The policies may also limit the duration of temporary ownership or exclude certain types of transactions. Understanding these limitations is critical to avoid potential complications or unforeseen consequences.
Temporary ownership of a life insurance policy can arise in various circumstances, such as during probate proceedings. While navigating these legal intricacies, understanding the fundamental components of a dish like ‘b love sauce’ might provide a comforting distraction. For those seeking the recipe’s ingredients, a helpful resource is available at b love sauce recipe ingredients. Ultimately, regaining policy ownership often hinges on resolving the underlying legal issues.
Comparison of Policies Among Insurance Companies
A comparison of the policies of different insurance companies concerning temporary ownership reveals substantial variations. These differences manifest in the specific clauses, the complexity of the procedures, and the requirements imposed upon the temporary owner. The level of transparency and communication also differs significantly.
Table Comparing Policies of Major Insurance Companies
| Insurance Company | Duration Limit (Months) | Required Documentation | Exceptions/Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| InsuraCorp | 6 | Identity verification, financial statement | Life-threatening illness, policy transfer to family member |
| Protector Insurance | 12 | Identity verification, legal authorization | Policy location change, pre-existing conditions |
| SecureShield | 9 | Identity verification, proof of relationship | Policy ownership dispute, fraudulent activity |
This table, while not exhaustive, provides a general overview of the differing policies among these three major companies. Further research is recommended for detailed understanding of each company’s specific requirements and limitations.
Illustrative Case Studies
A fragile thread of temporary ownership, woven through the somber tapestry of life’s uncertainties. The policy, a promise of solace, now becomes a burden, shifting like sand in the grasp of the bereaved. Each case study, a whispered lament, a testament to the complex dance between legal frameworks and human frailty.
Hypothetical Case Study of Temporary Ownership
Alistair, facing a sudden, debilitating illness, needed immediate access to funds. His life insurance policy, a legacy of his late father, held a substantial sum. To secure vital medical treatment, Alistair sought temporary ownership of the policy. This allowed him to borrow against its value, enabling timely medical care. The temporary transfer, carefully documented, preserved his father’s wishes while addressing Alistair’s immediate needs.
Case Study of a Successful Temporary Ownership Transfer
Eleanor, a devoted caregiver, was granted temporary ownership of her ailing mother’s life insurance policy. The transfer, meticulously executed according to the policy’s stipulations and local regulations, provided a steady stream of income to cover her mother’s escalating medical expenses. This timely action alleviated the family’s financial strain, proving that careful planning and adherence to legal processes can ease a difficult situation.
Case Study Illustrating Challenges with Temporary Ownership
Bernard, attempting a temporary ownership transfer to fund a business venture, encountered unexpected delays. A dispute arose over the policy’s beneficiary designation, hindering the smooth transition. The insurance company’s rigorous review procedures, while necessary for safeguarding their interests, caused significant stress and financial instability during a crucial period. The legal battle over beneficiary rights complicated matters further, illustrating the complexities involved in temporary ownership.
Case Study of Implications from Incorrect Procedures, Ownership of a life insurance policy may be temporarily
Caroline, desperate to provide for her children, hastily transferred temporary ownership of her life insurance policy without consulting legal counsel. This omission resulted in a voidable transfer. The insurance company, recognizing the procedural irregularities, refused to honor the temporary transfer. The unforeseen consequences left Caroline’s children financially vulnerable and underscored the critical need for legal guidance when navigating temporary ownership arrangements.
Legal Context of the Case Studies
These illustrative scenarios highlight the multifaceted legal considerations surrounding temporary ownership of life insurance policies. The legal framework, meticulously constructed, mandates specific procedures, documentation, and regulatory compliance. The terms of the policy itself, alongside state and federal laws, define the permissible scope of temporary ownership transfers. Failure to adhere to these intricate rules can lead to substantial complications, ultimately jeopardizing the policyholder’s intentions.
The legal counsel plays a critical role in ensuring compliance and minimizing potential risks associated with temporary transfers.
- Policy Provisions: The policy’s specific terms and conditions dictate the rules governing temporary ownership transfers, including the duration, terms, and requirements for such arrangements. A meticulous review of the policy’s fine print is paramount.
- State and Federal Laws: State insurance laws and federal regulations Artikel specific guidelines and procedures for life insurance policy transfers. Compliance with these legal stipulations is essential for the validity of any temporary ownership arrangement.
- Documentation: Comprehensive documentation is crucial to the legitimacy of any temporary ownership transfer. This includes properly executed forms, notarization, and evidence of the policyholder’s authority.
- Insurance Company Policies: Each insurance company may have internal procedures for temporary ownership transfers. Familiarity with these policies is vital to ensure a smooth and compliant transition.
Final Thoughts: Ownership Of A Life Insurance Policy May Be Temporarily
In conclusion, temporary ownership of a life insurance policy, while often necessary in specific situations, carries distinct legal and practical implications. Navigating these complexities requires careful attention to the specific terms and conditions, and a thorough understanding of the relevant legal frameworks and insurance company policies. This guide aims to equip readers with the knowledge to make informed decisions regarding temporary ownership arrangements.
FAQ Corner
What are the common scenarios where temporary ownership of a life insurance policy arises?
Temporary ownership often arises during loan arrangements, trust setups, or when a policy is pledged as collateral. Other situations may include a policy being held in a conservatorship or guardianship.
How does temporary ownership differ from beneficiary designations?
Temporary ownership involves a transfer of ownership rights, while beneficiary designations determine who receives the policy’s death benefit. Temporary ownership may change the policyholder’s rights, but not necessarily who receives the death benefit.
What are the potential tax implications of temporary ownership?
Tax implications can vary based on jurisdiction and the specific circumstances of the temporary ownership arrangement. It’s essential to consult with a tax professional for personalized guidance.
What documents are required for a temporary ownership transfer?
Specific documents vary by insurance company and jurisdiction, but typically include the policyholder’s consent, the temporary owner’s identification, and supporting documentation related to the reason for temporary ownership.
