Recovery Housing Levels 3.1 marks a crucial step in the journey to sustainable recovery. This level provides a supportive environment for individuals navigating the complexities of their recovery, offering a blend of structured programs and personalized support. Understanding the nuances of Level 3.1 is vital for those seeking resources or supporting those in need. This detailed exploration delves into the defining characteristics, support services, and program structures associated with this level of care.
This guide will Artikel the specific needs and placement criteria for Level 3.1, providing a comprehensive understanding of the support systems in place. We will also examine the common challenges faced by residents and strategies to overcome them, all while highlighting the importance of community engagement and external resources.
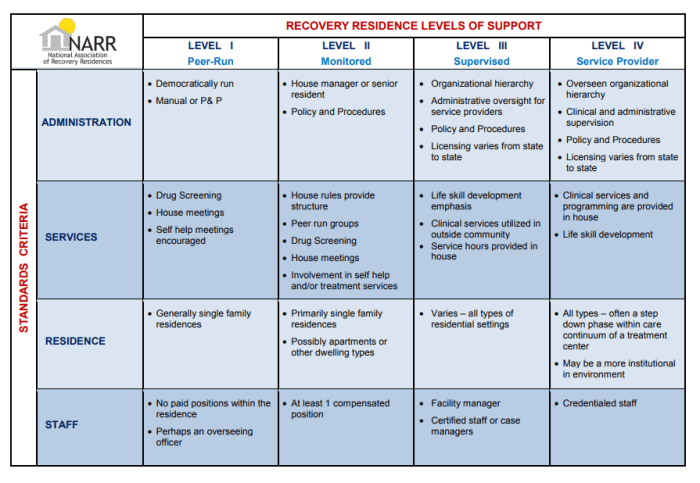
Defining Recovery Housing Levels 3.1
Recovery housing levels, like 3.1, are designed to provide a structured environment for individuals navigating the complexities of recovery. These levels are progressively more independent, requiring greater self-management skills from residents as they move up. Level 3.1 represents a significant step towards greater autonomy and independence while maintaining crucial support.Recovery Housing Level 3.1 is characterized by a higher degree of self-sufficiency compared to lower levels, while still offering substantial support to residents.
This level typically provides a balance between structured living and increasing personal responsibility, aiming to cultivate the skills necessary for independent living. The emphasis is on fostering stability, promoting self-care, and enhancing life skills.
Recovery housing levels 3.1 are a crucial part of the support system for those in need. Knowing the local resources available, like those provided by schoenbauer funeral home montgomery mn , is vital during tough times. This kind of community support is important to ensure successful transitions back into stable living environments, especially considering the complexity of recovery housing levels 3.1.
Characteristics and Criteria
Level 3.1 recovery housing often involves a supportive, yet less intensive, environment compared to higher levels of care. Residents at this level generally demonstrate a solid understanding of their recovery needs and have a history of successful engagement in treatment programs. They are expected to adhere to the house rules and participate actively in their recovery plan. Essential criteria for admission usually include a stable housing history, a proven ability to maintain personal hygiene and safety, and a commitment to ongoing recovery support.
Support Services and Amenities
A comprehensive array of support services are crucial at Level 3.1. These include access to individual and group therapy sessions, case management, relapse prevention strategies, and guidance on life skills. The level of supervision is typically reduced compared to lower levels, but remains available as needed. Amenities often include shared kitchen and laundry facilities, recreational areas, and access to community resources.
Emphasis is placed on providing opportunities for social interaction and building a supportive network.
Goals and Expected Outcomes
The overarching goal for residents at Level 3.1 is to develop the skills necessary for independent living. Expected outcomes include improved self-care routines, enhanced coping mechanisms, increased social skills, and progress towards financial independence. Residents are encouraged to actively participate in vocational training or job searching, with ongoing support from case managers. Residents are also encouraged to maintain their connections with support networks and community resources.
Types of Individuals Appropriate for Level 3.1
Individuals suitable for Level 3.1 recovery housing have typically demonstrated a significant level of progress in their recovery journey. They have established a strong foundation in their recovery plan and are able to navigate the challenges of independent living with ongoing support. Examples include individuals who have completed initial treatment programs, are demonstrating stability, and are prepared to take on greater responsibility.
This level is also well-suited for those who have experienced setbacks but are committed to rebuilding their lives.
Key Differences Between Levels 3.1 and 3.0
| Characteristic | Level 3.1 | Level 3.0 |
|---|---|---|
| Level of Supervision | Reduced, but available as needed | More intensive, structured supervision |
| Resident Responsibility | Higher, focused on self-management | Lower, with more direct support |
| Support Services | Comprehensive, including case management, life skills training, and relapse prevention | Basic, focused on immediate needs and stabilization |
| Housing Environment | More independent, with increasing autonomy | Highly structured and supportive |
| Resident Profile | Demonstrates significant progress in recovery, capable of greater self-sufficiency | Demonstrates a need for ongoing support, recent progress in recovery, and less independent living skills |
Assessing Needs and Placement
Level 3.1 recovery housing presents a crucial transition phase. Residents are moving towards greater independence and self-sufficiency. This section details the assessment process, emphasizing factors to consider when determining suitability and strategies for successful transitions. It also Artikels the monitoring process to ensure residents’ well-being and progress.
Factors Determining Suitability for Level 3.1 Housing
Residents are carefully evaluated to determine if they are ready for the increased responsibilities and independence of level 3.1 housing. Key factors include demonstrating a consistent pattern of progress in treatment and recovery programs. This involves a clear understanding of the individual’s needs, including their living skills, social skills, and coping mechanisms. Additionally, residents should show evidence of stability in their daily routines and relationships.
Their motivation for independent living and capacity for self-care are also significant considerations.
Evaluating Resident Needs and Progress
A comprehensive needs assessment is essential. This includes reviewing the resident’s treatment history, identifying current support needs, and assessing their progress in key areas like sobriety, managing finances, and maintaining healthy relationships. Regular progress evaluations are conducted to track improvements and any setbacks. These evaluations typically include direct observation of the resident’s behavior and interactions, interviews with the resident and support staff, and review of relevant documentation.
Consistent monitoring ensures adjustments can be made to support the resident’s specific needs.
Indicators of Successful Transition to Level 3.1
Successful transition to level 3.1 housing is marked by a range of positive indicators. These include maintaining sobriety, managing finances responsibly, demonstrating improved living skills, actively participating in community activities, and building healthy relationships. The resident should also display a commitment to self-care and personal growth. Furthermore, positive interactions with peers and staff in the community setting suggest a successful transition.
For example, a resident consistently attending support groups and demonstrating engagement with the community suggests a positive transition.
Tracking and Monitoring Resident Progress in Level 3.1
A structured tracking system is critical to monitor progress and identify potential issues early. This system should document daily activities, including attendance at meetings, progress in self-care, and engagement with community resources. Staff should document any challenges and the support provided. Regular reviews of the resident’s progress are conducted, incorporating input from the resident, support staff, and potentially, family members.
Data collected will inform necessary interventions or adjustments in support systems.
Comparing and Contrasting Needs Assessment Criteria Across Housing Levels
Needs assessment criteria vary based on the specific level of support required. Level 3.1 housing requires a higher level of self-sufficiency than lower levels, such as 2.0 or 1.0. Lower levels often focus on basic needs and stabilization, whereas level 3.1 focuses on independent living skills and community integration. Comparison of criteria across levels allows for a smooth transition between levels and ensures residents are progressing appropriately.
For instance, a resident moving from level 2.0 to level 3.1 might exhibit an increased capacity for self-care, a more stable living environment, and a stronger support network.
Services and Supports at Level 3.1
Level 3.1 recovery housing provides a crucial stepping stone for individuals transitioning from more intensive care settings or independent living. This level focuses on fostering stability and building crucial skills for long-term recovery and community integration. It’s designed to provide a supportive environment that gradually reduces direct supervision while promoting self-sufficiency.
Essential Services and Support Programs
Level 3.1 housing incorporates a comprehensive suite of services and supports tailored to meet the unique needs of residents. These programs are designed to address various aspects of recovery, from practical life skills to emotional well-being. Key components include case management, individual counseling, and group therapy sessions. Access to medical and mental health professionals is also integral, enabling timely interventions and addressing potential setbacks.
Transportation assistance, and access to educational and vocational resources are also frequently provided.
Individualized Support Plans
Individualized Support Plans (ISPs) are pivotal in ensuring personalized care for residents at level 3.1. These plans are dynamic documents that Artikel specific goals and strategies for each resident, reflecting their individual needs, strengths, and preferences.
- Examples of ISP components include:
- Identifying specific goals, such as improving housing stability, managing finances, or obtaining employment.
- Developing a relapse prevention plan, which may include strategies for coping with triggers, support networks, and early intervention strategies.
- Outlining a plan for gradual reduction in supervision and increased independence, progressing towards a more self-directed lifestyle.
- Incorporating strategies for improving social skills, such as communication and conflict resolution.
- Creating a personalized schedule for therapy sessions, medication management, and other essential appointments.
Community Integration and Engagement
Community integration is paramount at level 3.1. This fosters a sense of belonging and enables residents to re-establish connections with their surroundings, participate in social activities, and rebuild their social support network. This can involve connecting residents with community resources, such as support groups, volunteer opportunities, or recreational activities.
Role of Staff and Mentors
Staff and mentors play a crucial role in guiding residents toward achieving their goals. They act as a supportive network, offering encouragement, guidance, and assistance. Mentors are often individuals with lived experience who provide invaluable insight and understanding. The staff’s role involves facilitating access to resources, monitoring progress, and adapting support as needed. They also promote a sense of community and camaraderie among residents.
Comparison of Support Levels, Recovery housing levels 3.1
| Level | Frequency of Support (Example) | Types of Support (Example) |
|---|---|---|
| Level 3.1 | Weekly individual meetings, bi-weekly group sessions, as needed crisis intervention. | Case management, individual therapy, medication management, job training, transportation assistance. |
| Level 3.2 | Monthly check-ins, as needed crisis intervention, support groups as needed. | Case management, group therapy, job coaching, limited transportation assistance. |
| Level 3.3 | Bi-monthly check-ins, occasional support groups. | Case management, limited therapy, access to community resources. |
Program Structure and Outcomes
Level 3.1 recovery housing programs are designed to provide a supportive and structured environment for residents navigating significant challenges in their recovery journeys. The program structure prioritizes safety, stability, and fostering a sense of community while encouraging personal growth and self-sufficiency. These programs understand that a holistic approach is necessary, and it is more than just a place to live.The key to success lies in a well-defined program structure, coupled with a dedicated team of professionals who provide the necessary services and support.
This approach aims to create a positive feedback loop, where residents’ engagement with the program translates into positive outcomes. Structured activities are carefully crafted to promote recovery, address individual needs, and help residents transition back into independent living.
Typical Program Structure and Daily Routines
The daily routines at Level 3.1 recovery housing are designed to promote a sense of normalcy and routine, helping residents regain control over their lives. A typical day might involve a structured schedule that includes meal preparation and consumption, personal hygiene activities, individual and group therapy sessions, recreational activities, and educational workshops. This structure provides a framework for the residents to gradually regain control and develop healthy coping mechanisms.
The specific structure can vary based on individual needs and preferences.
Structured Activities Promoting Recovery and Wellness
Structured activities are crucial in Level 3.1 programs. They’re not just about keeping residents busy; they’re designed to address specific needs and promote recovery and well-being. These activities could include mindfulness exercises, art therapy sessions, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) groups, vocational training workshops, and recreational activities like group sports or outdoor outings. The goal is to equip residents with practical skills and tools for navigating daily life while fostering emotional well-being.
Methods for Evaluating Program Effectiveness
Evaluating the effectiveness of a Level 3.1 program requires a multi-faceted approach. Key performance indicators (KPIs) should include measures of resident engagement, relapse rates, housing stability, and employment outcomes. Regular assessments and feedback from residents and staff are essential for identifying areas of improvement and ensuring the program remains relevant to the needs of the individuals served. These evaluations should include both quantitative data (e.g., attendance rates, employment statistics) and qualitative data (e.g., resident feedback, staff observations).
Challenges and Addressing Them
Challenges are inevitable in any recovery program. Residents might experience setbacks, relapse triggers, or interpersonal conflicts. A proactive approach is essential. The program should have clear protocols for addressing these challenges, including crisis intervention plans, access to mental health professionals, and conflict resolution strategies. A strong support system that includes both staff and peer support groups can be invaluable in navigating these difficulties.
A key element is early intervention to prevent potential issues from escalating.
Measurable Outcomes and Metrics
The following table Artikels the measurable outcomes and metrics used to track resident progress in Level 3.1 recovery housing.
| Outcome | Metric | Target |
|---|---|---|
| Engagement in Program Activities | Average weekly attendance at program activities | 80% |
| Relapse Rate | Percentage of residents experiencing relapse within a specific time frame | Less than 15% |
| Housing Stability | Number of months continuously residing in the program | 12 months |
| Employment Outcomes | Percentage of residents obtaining employment | 60% |
| Improved Mental Well-being | Reduction in reported symptoms of anxiety and depression (measured via standardized assessments) | 30% decrease |
Addressing Specific Challenges
Level 3.1 recovery housing presents unique challenges, requiring tailored strategies for success. Residents often grapple with a complex interplay of emotional, social, and practical difficulties stemming from their past experiences. Understanding these challenges and proactively developing solutions are crucial for fostering positive outcomes.Addressing these challenges necessitates a multifaceted approach, combining evidence-based practices with individualized support. This section details common struggles, relapse prevention, safety protocols, conflict resolution, and crisis management within the 3.1 housing environment.
Common Challenges and Potential Solutions
Residents at Level 3.1 frequently experience intense cravings, triggers, and emotional dysregulation. These issues often lead to difficulties with interpersonal relationships, maintaining sobriety, and navigating daily life. Potential solutions include structured group therapy, individual counseling, and access to peer support networks. A key component of addressing these challenges is recognizing the individual’s unique needs and tailoring interventions accordingly.
Recovery housing levels 3.1 often require specialized support, and finding the right insurance can be tricky. Fortunately, Care n Care Insurance in Fort Worth, TX, care n care insurance fort worth tx , specializes in helping people navigate these complex situations. Ultimately, understanding options like this can help ensure a smoother path toward stable housing for everyone involved in recovery levels 3.1.
Relapse Prevention Strategies
Relapse prevention is paramount at Level 3.1. This involves proactively identifying potential triggers, developing coping mechanisms, and establishing a strong support system. A comprehensive relapse prevention plan should include strategies for managing stress, recognizing warning signs, and practicing self-care techniques. This proactive approach empowers residents to navigate challenges and reduce the likelihood of relapse. Identifying and addressing underlying triggers, such as trauma, is vital.
Ensuring Resident Safety and Well-being
Ensuring resident safety and well-being is paramount. Comprehensive safety protocols must be implemented, including clear guidelines for handling conflicts, access to crisis intervention services, and ongoing monitoring. This includes creating a secure and supportive environment that fosters trust and encourages open communication. Regular check-ins, individual support, and access to mental health professionals are essential components.
Conflict Resolution and Interpersonal Skills
Conflict resolution and interpersonal skills are essential life skills. Providing training and workshops in communication, empathy, and conflict resolution techniques can greatly improve residents’ ability to navigate social interactions effectively. This can include role-playing exercises, group discussions, and practical application of skills in real-life scenarios. Building healthy communication patterns is crucial to maintain a positive and supportive living environment.
Crisis Management Process
Effective crisis management is vital for the safety and well-being of residents. A structured process should be in place for responding to crises, ensuring prompt intervention and support.
| Crisis Stage | Action Steps |
|---|---|
| Identification | Recognize signs of escalating distress; observe changes in behavior, mood, or communication. Document the incident. |
| Intervention | Immediately contact support staff, including case managers and mental health professionals. Assess the situation and identify immediate needs. Follow established protocols. |
| Support | Provide emotional support and reassurance. Offer coping mechanisms and strategies. Ensure physical safety is maintained. Arrange for medical assistance if necessary. |
| Follow-up | Debrief with the resident and support staff. Identify contributing factors and develop strategies for preventing future crises. Document the entire incident and the response. Ensure access to necessary resources and follow-up support. |
Community and External Resources: Recovery Housing Levels 3.1
Community partnerships are crucial for the success of residents in Level 3.1 recovery housing. These partnerships create a supportive network that extends beyond the walls of the facility, providing a range of resources and opportunities that residents need to maintain and advance their recovery. This approach fosters a sense of belonging and empowers residents to navigate the complexities of life outside the program.Effective recovery housing programs recognize that residents need access to a multitude of services beyond the core program.
These external resources can provide crucial support in areas such as employment, healthcare, housing, and legal aid. Connecting residents with appropriate community services is a vital component of the overall recovery process. A well-structured system for connecting residents with these services ensures that they receive the necessary assistance at the right time.
Importance of Community Partnerships
Community partnerships are essential for Level 3.1 residents. These collaborations can provide a comprehensive network of support, increasing residents’ chances of sustained recovery. Partnerships can offer specialized expertise and resources that may not be readily available within the housing program itself. Furthermore, they foster a sense of community belonging, encouraging residents to engage with their surroundings and develop meaningful connections.
Key Community Resources
Several key resources can significantly support residents in Level 3.1 recovery housing. These resources include employment agencies, healthcare providers, housing assistance organizations, legal aid services, and social support groups. These organizations offer essential services that can help residents address their needs, navigate the challenges of recovery, and transition into independent living.
Connecting Residents with Relevant Services
A structured process for connecting residents with these services is vital. This process should involve a dedicated staff member or team responsible for identifying the specific needs of each resident. The process should also incorporate a system for tracking resident engagement with community services and evaluating the effectiveness of these connections. This ensures residents receive the appropriate assistance and the necessary support to stay on track with their recovery.
A well-defined process ensures that residents are not overwhelmed and receive timely and appropriate support.
Examples of External Resource Contributions
A local employment agency, for example, can help a resident find suitable employment opportunities, providing job training and resume building services. A mental health clinic can offer crucial ongoing support, and a housing organization can assist with finding and securing stable housing. These examples demonstrate how external resources can contribute directly to resident success, enhancing their well-being and facilitating their return to independent living.
Table of External Resources and Services
| Resource | Services Provided |
|---|---|
| Local Employment Agencies | Job placement, job training, resume building, career counseling |
| Mental Health Clinics | Therapy, medication management, support groups |
| Housing Assistance Organizations | Finding affordable housing, rental assistance, support in navigating housing processes |
| Legal Aid Services | Legal advice and representation, assistance with legal issues, navigating legal systems |
| Social Support Groups | Peer support, encouragement, community building, shared experiences |
Last Point

In conclusion, Recovery Housing Levels 3.1 represent a significant step toward successful recovery. By understanding the characteristics, support systems, and program structure of Level 3.1, we can better equip individuals with the tools and resources they need to thrive. The emphasis on community integration, relapse prevention, and individualized support plans creates a comprehensive approach to recovery, ensuring residents have the best chance for long-term success.
Clarifying Questions
What are the typical daily routines for residents in Level 3.1 housing?
Daily routines at Level 3.1 housing often include structured activities like group therapy sessions, individual counseling, and vocational training, alongside opportunities for self-care and personal growth. Specific routines will vary based on the individual resident’s needs and the program’s structure.
What kind of support plans are tailored to residents in Level 3.1?
Individualized support plans for Level 3.1 residents are crucial and incorporate specific goals, strategies, and timeframes for progress. These plans address each resident’s unique needs, including therapy, medication management (if applicable), and life skills development.
How is resident progress tracked and monitored in Level 3.1 housing?
Progress is monitored through regular assessments, feedback from staff and mentors, and self-reflection by the resident. Data collection and evaluation methods are used to track progress and identify areas for improvement, ensuring the program is effective.
What are some common challenges faced by residents at Level 3.1 and how are they addressed?
Common challenges include social isolation, relapse triggers, and financial instability. These challenges are addressed through comprehensive support systems that include peer support, financial assistance programs, and community integration strategies.
